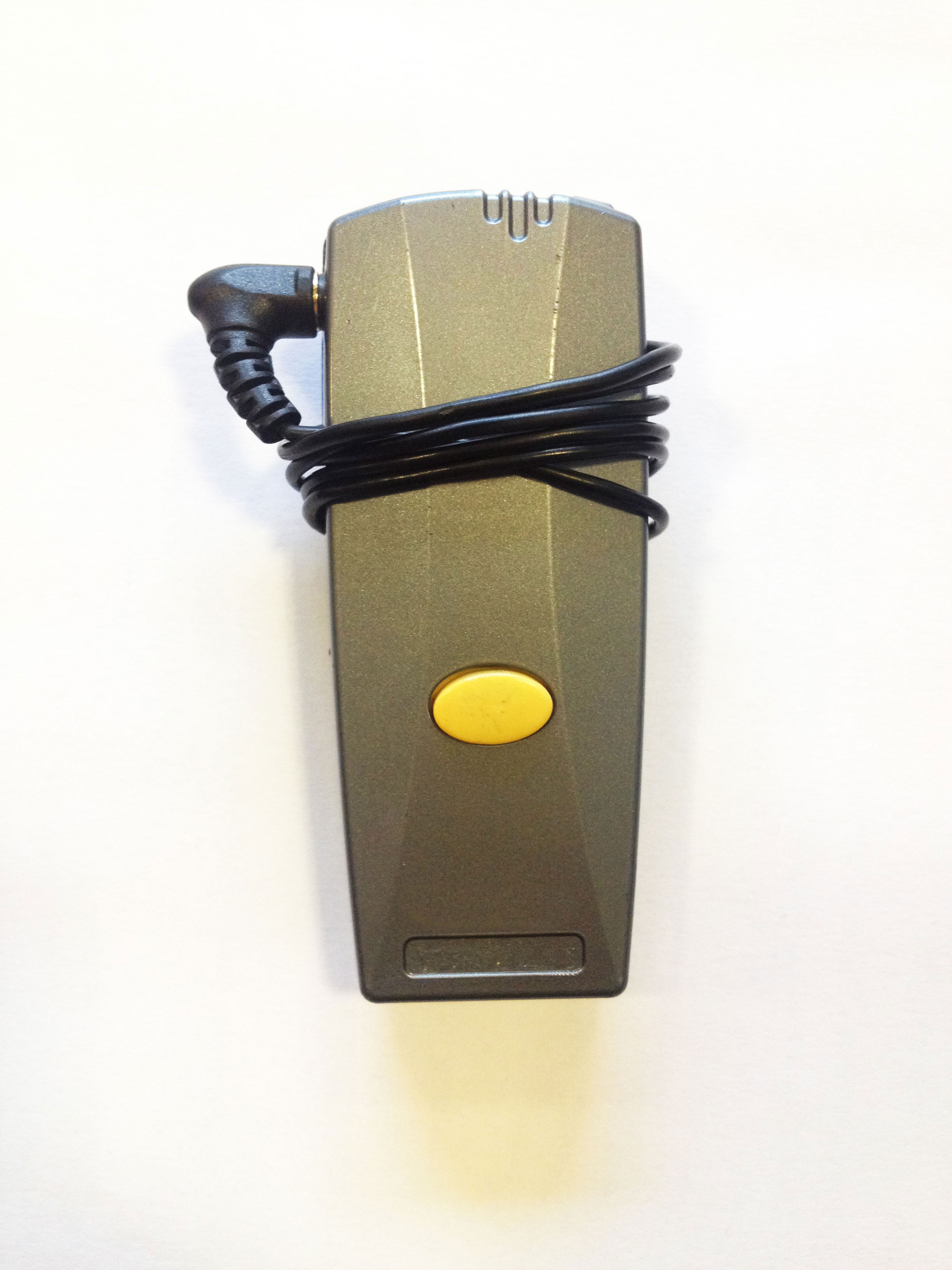
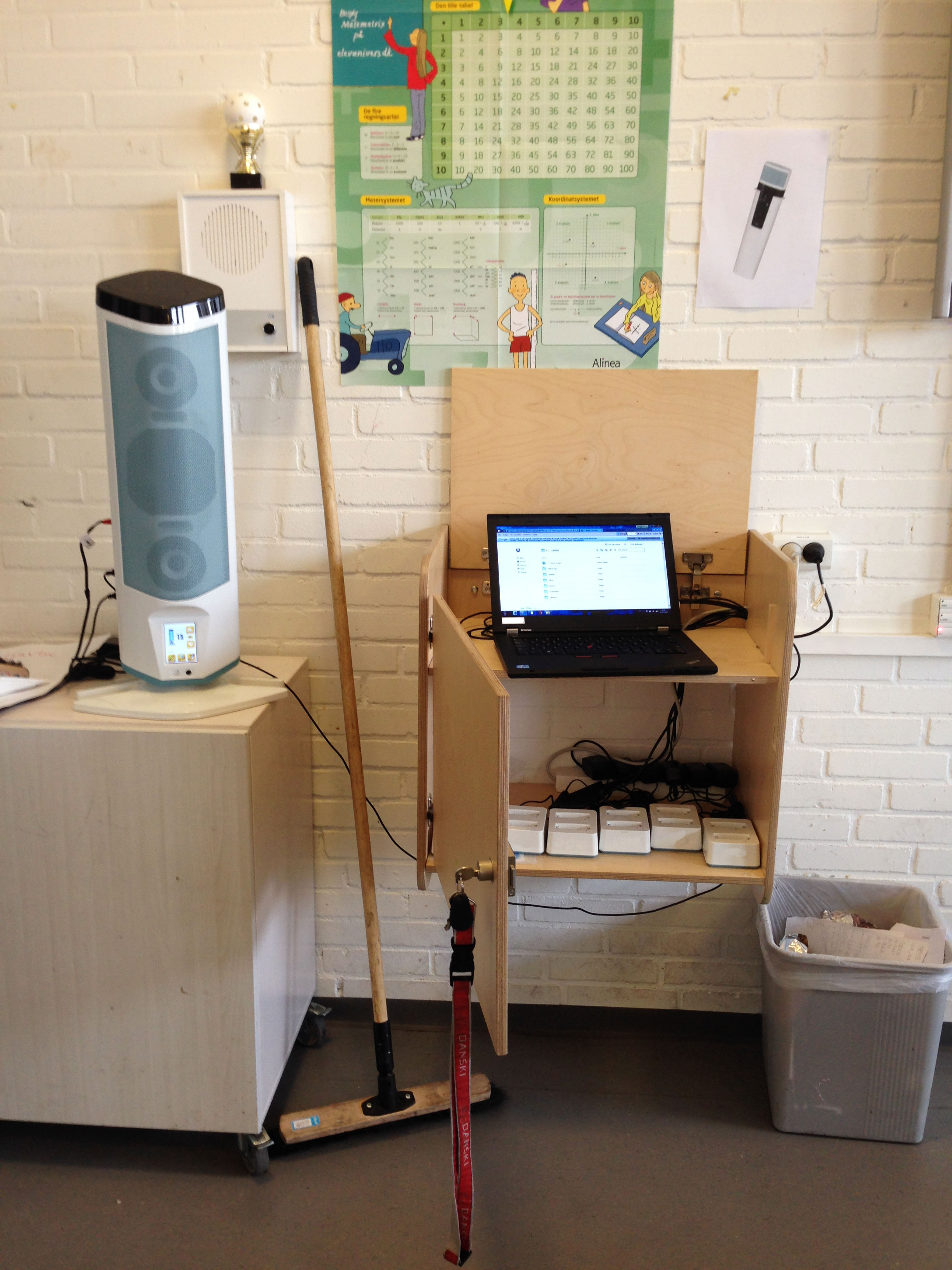
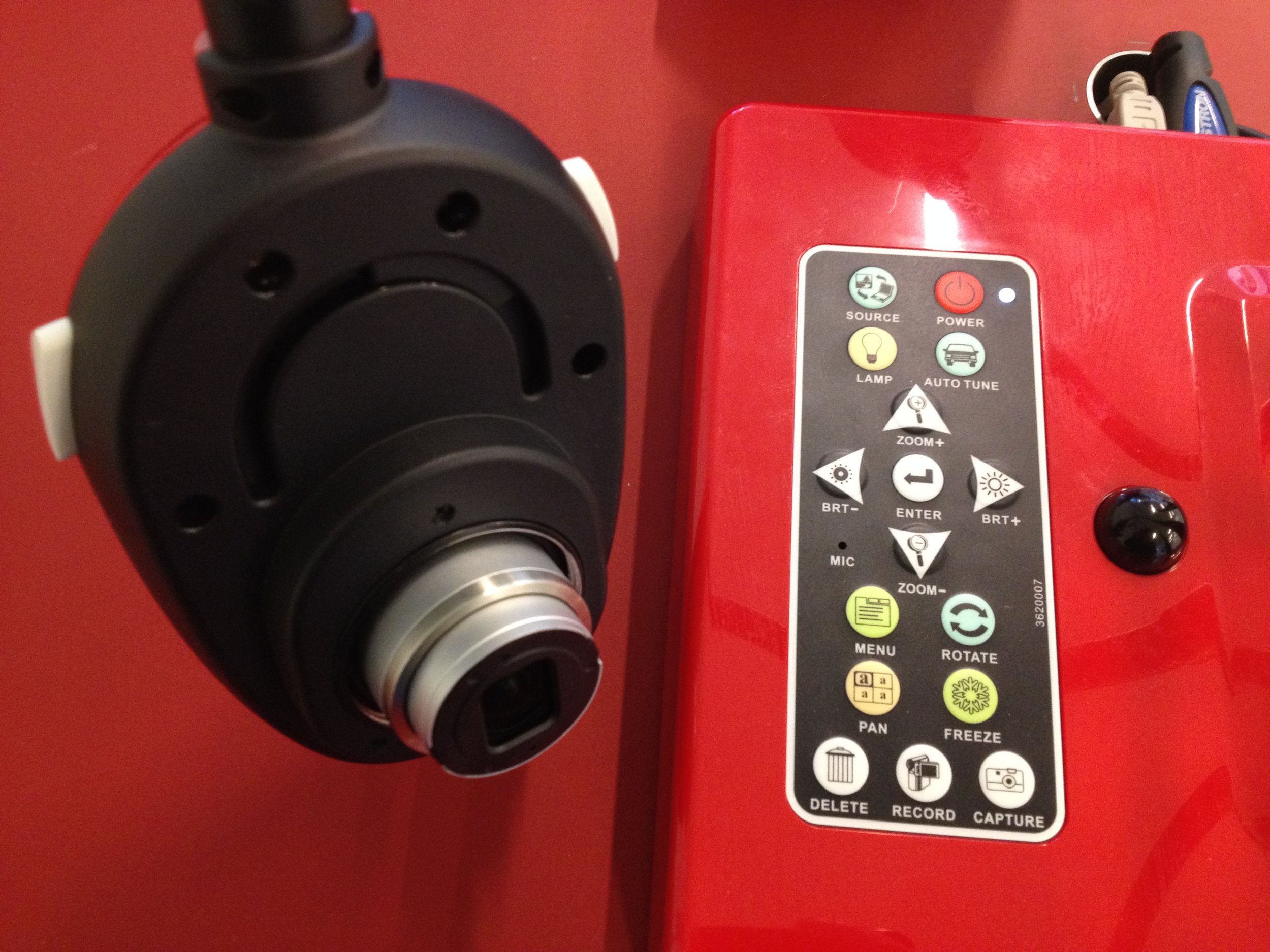
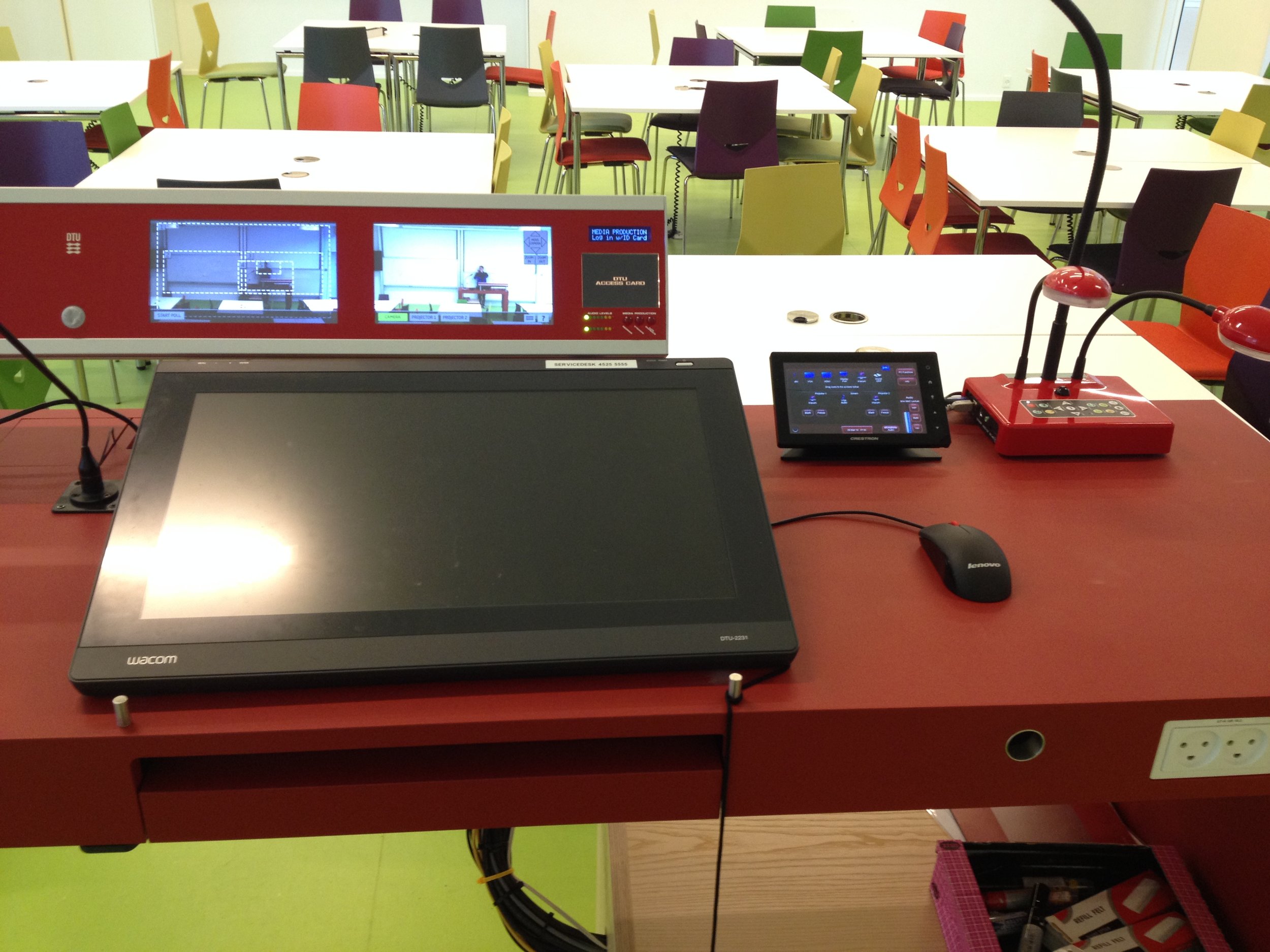
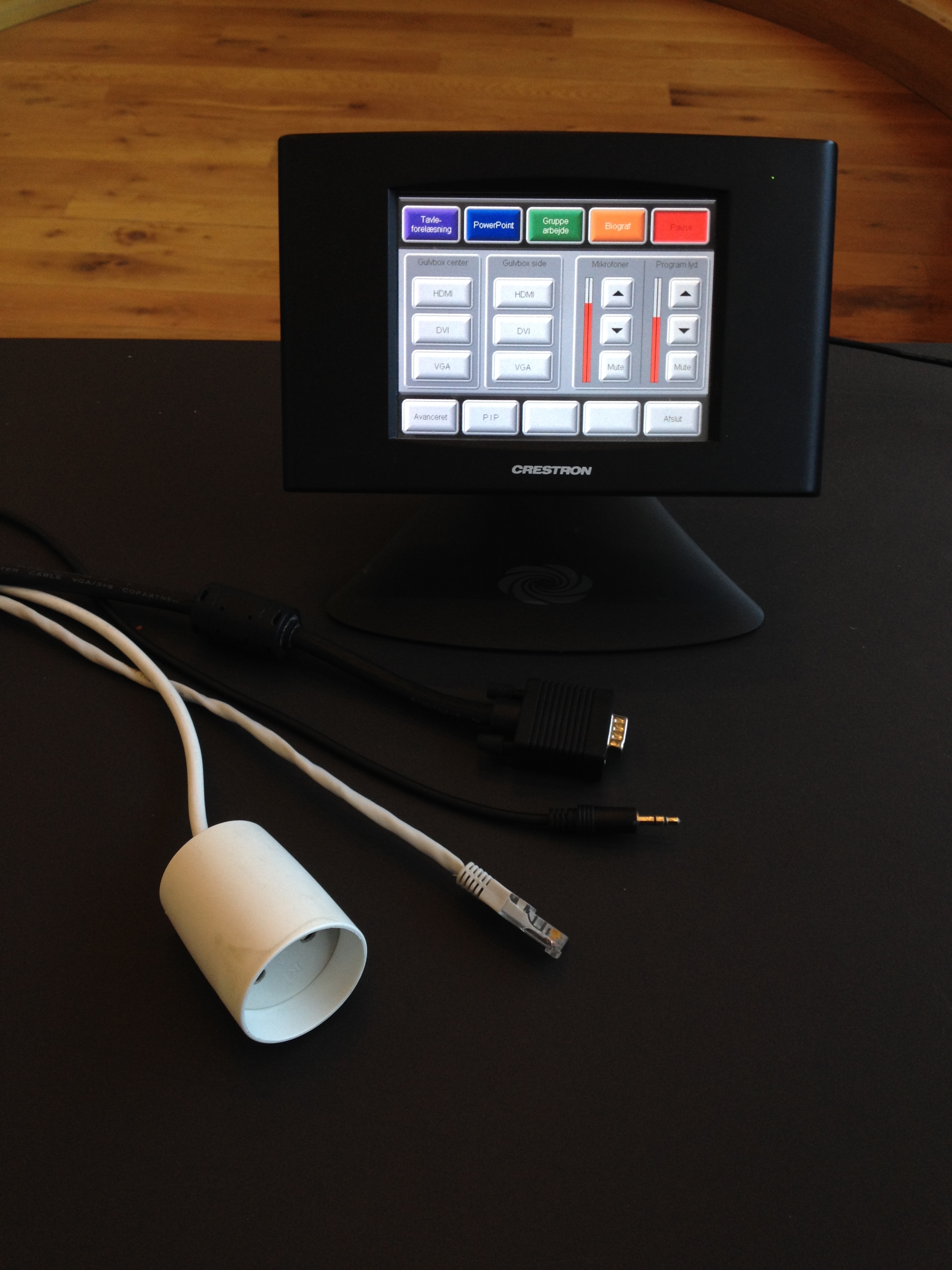
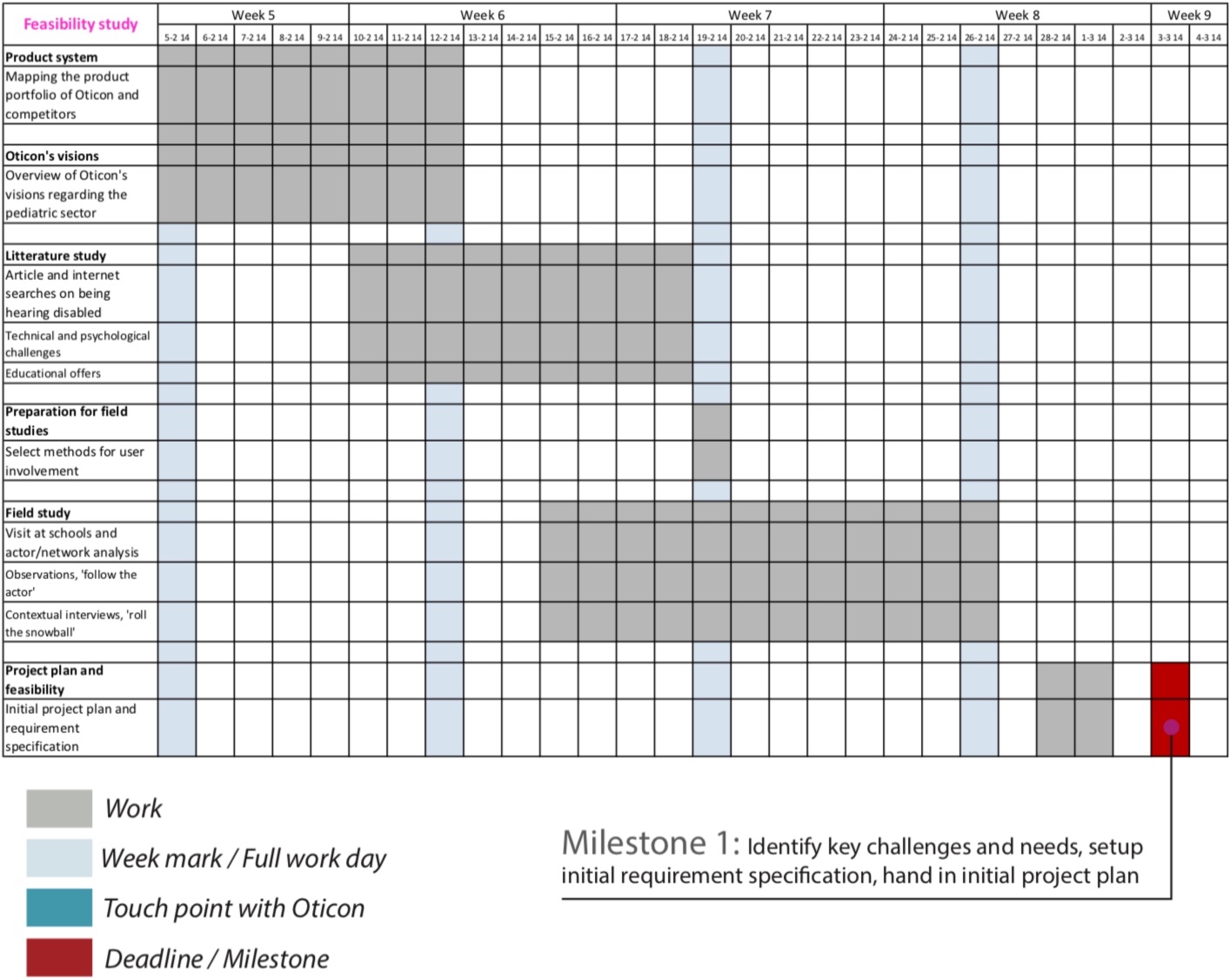
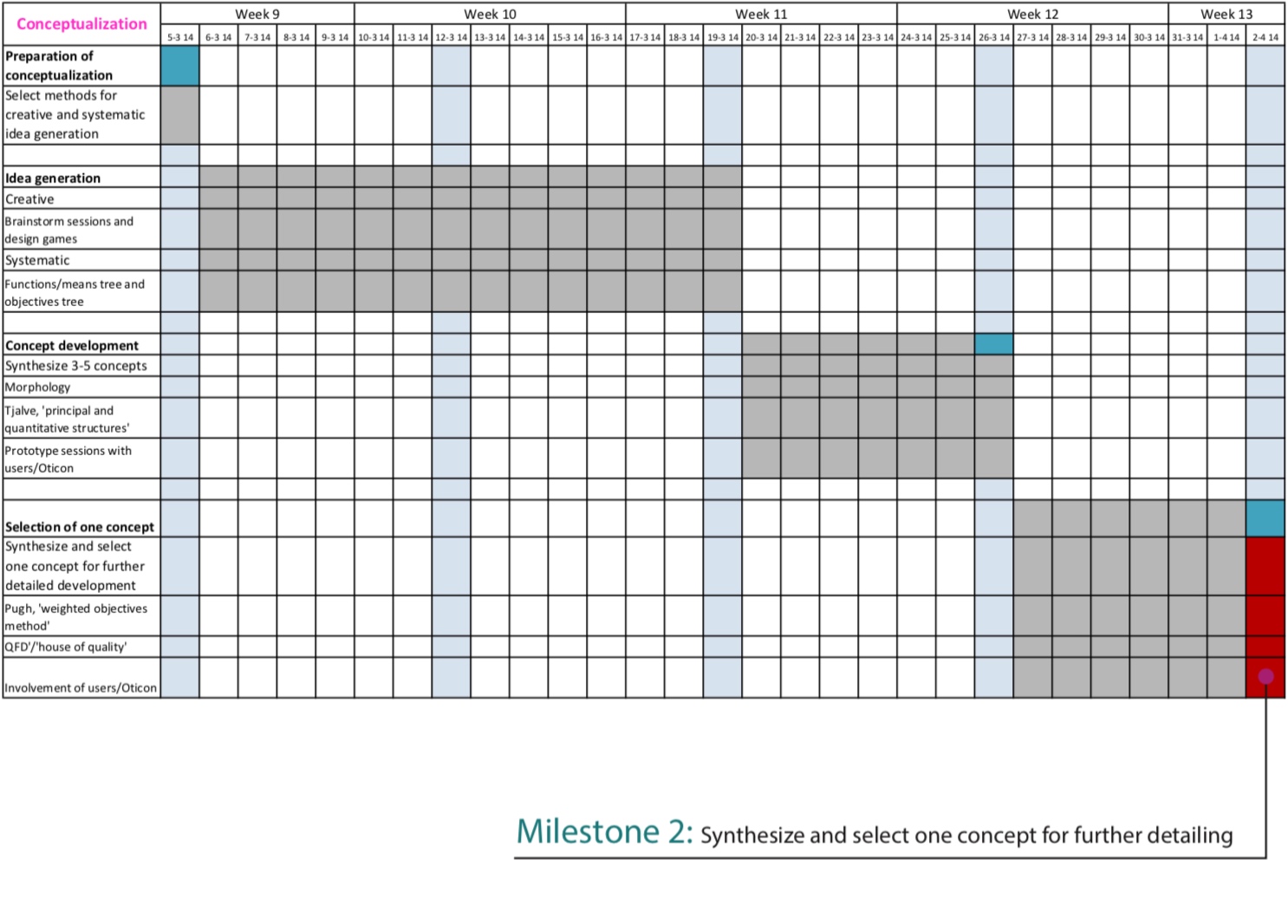
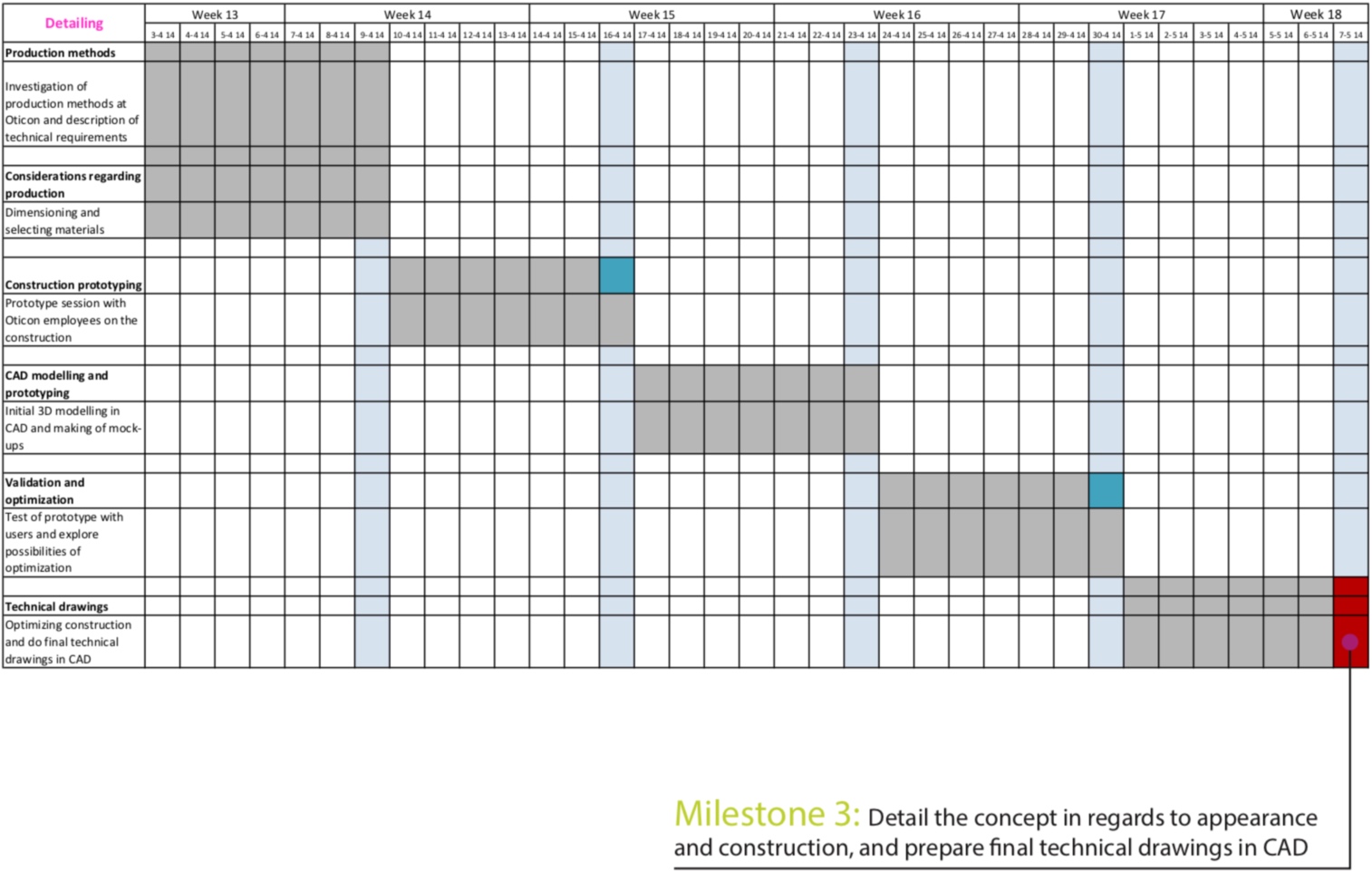
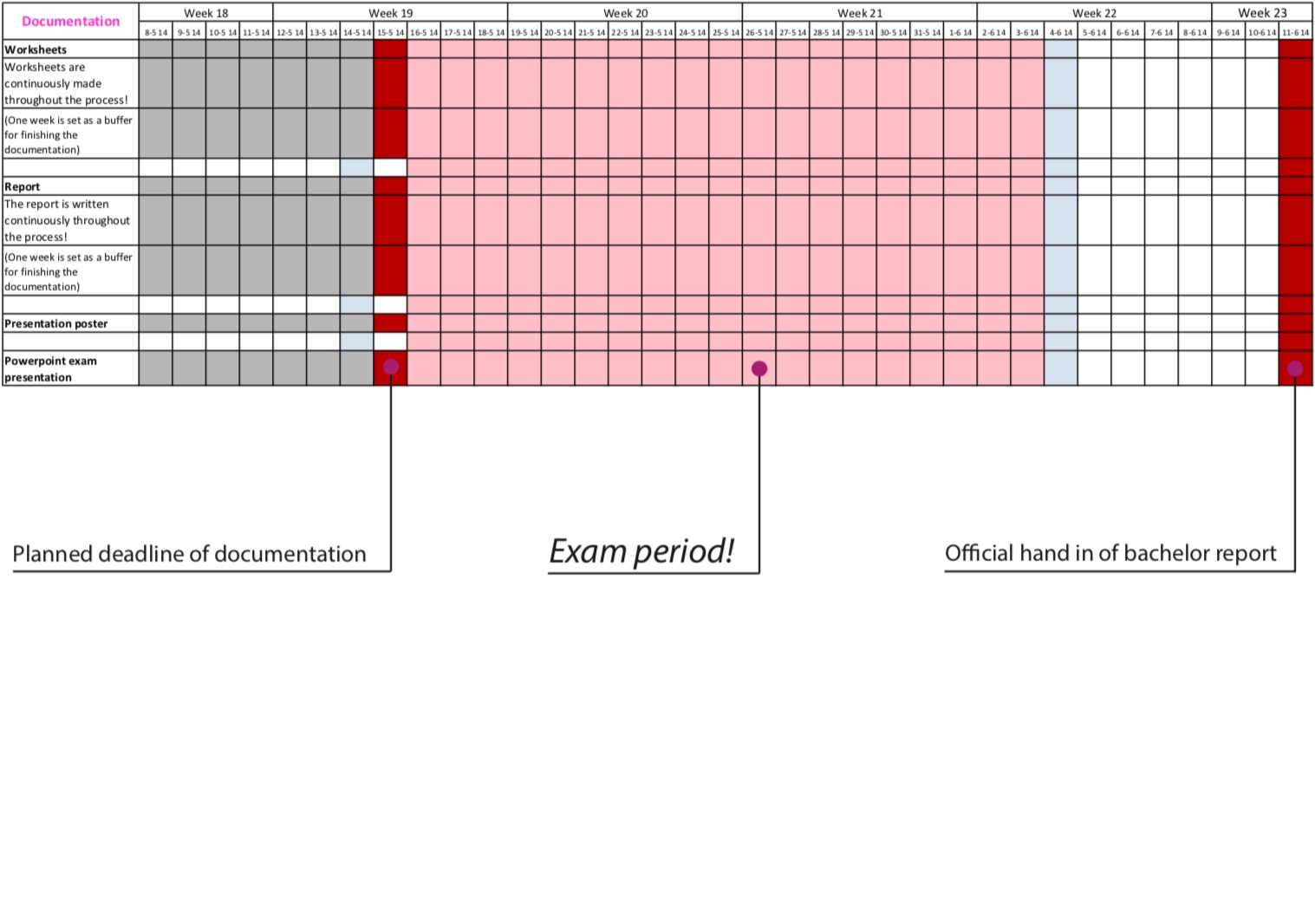
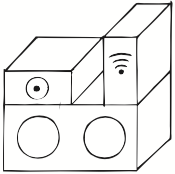
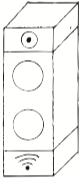
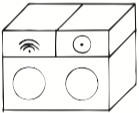
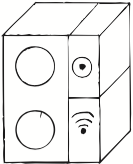
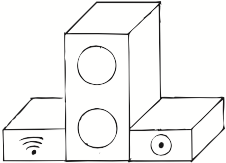
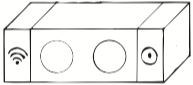
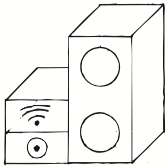
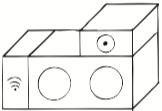
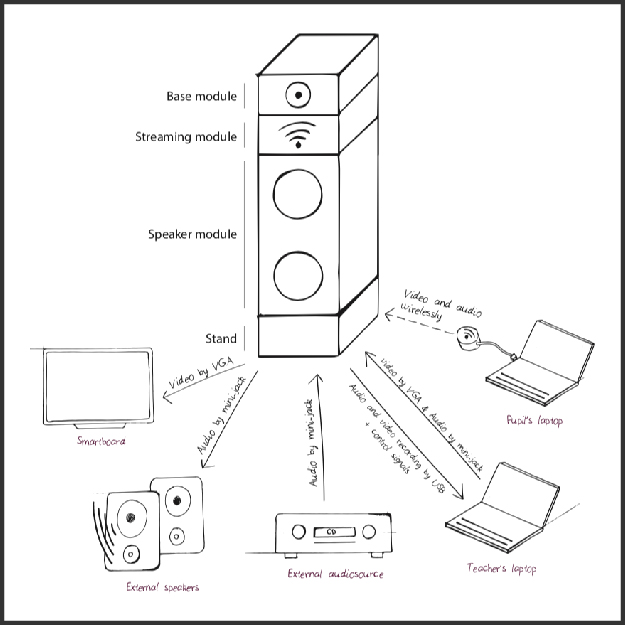
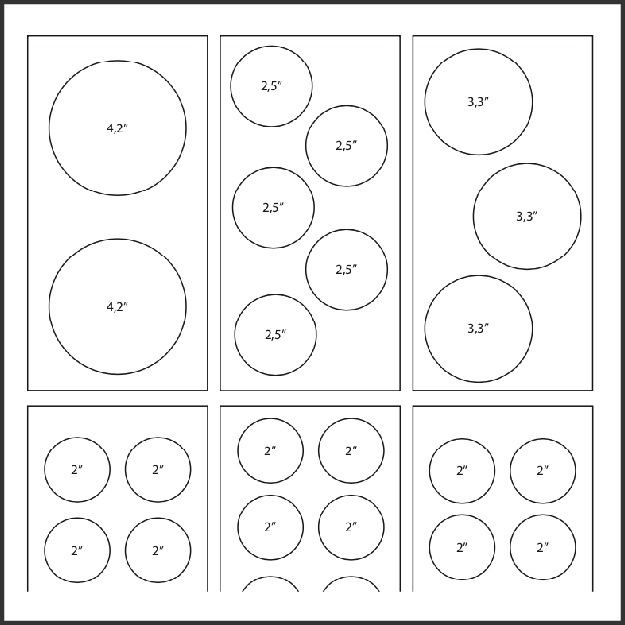
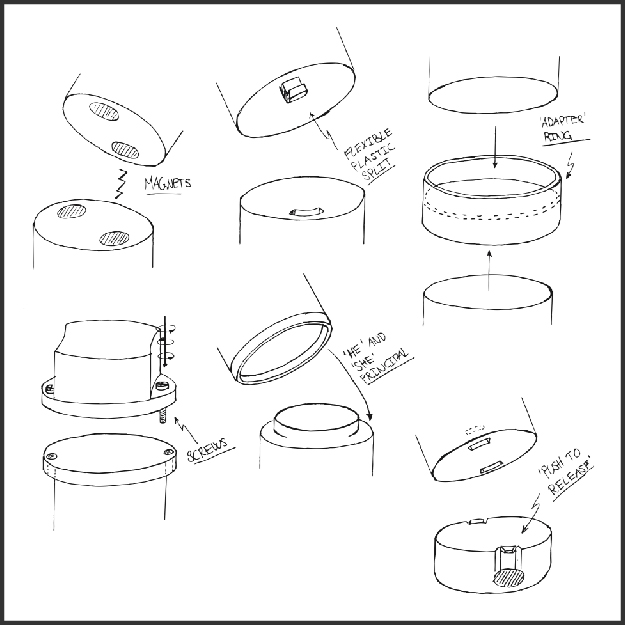
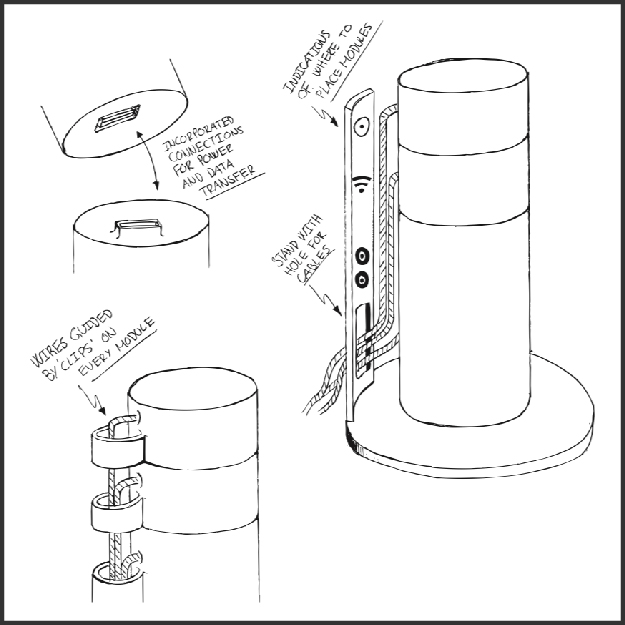
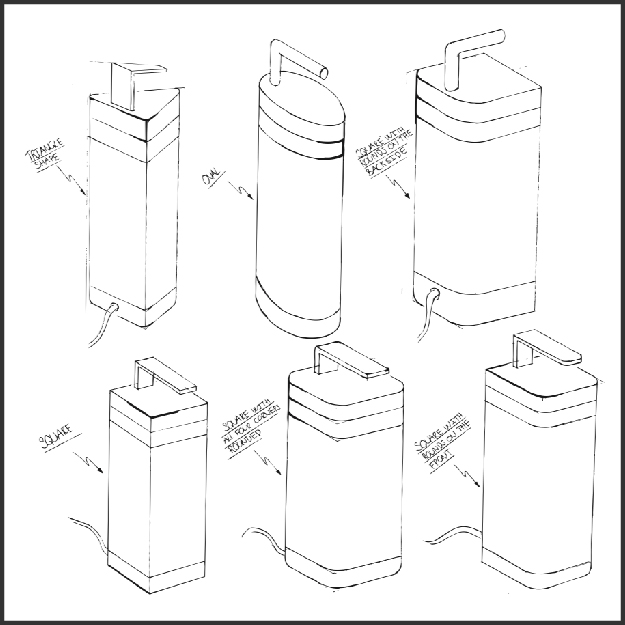
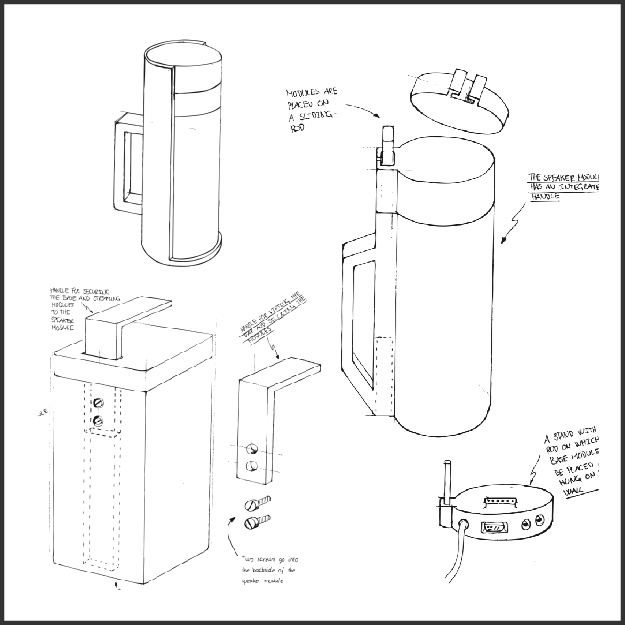
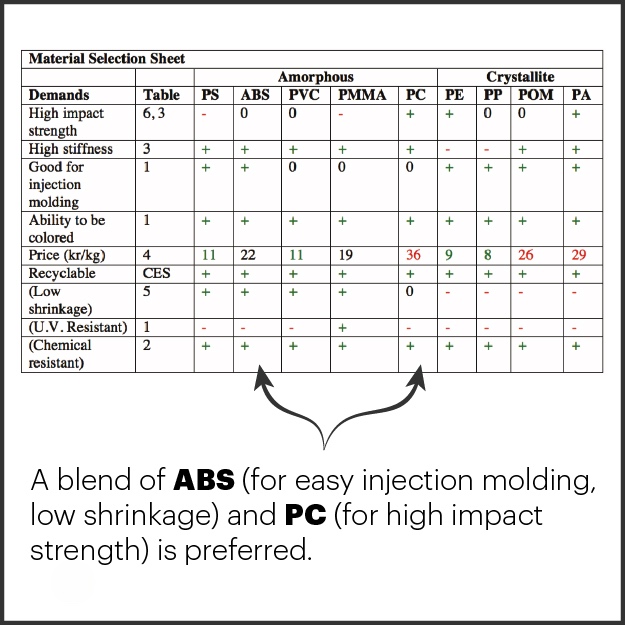
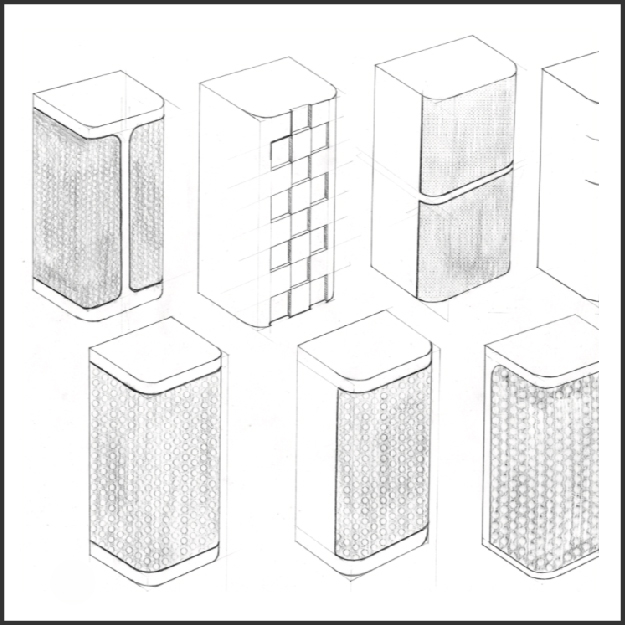
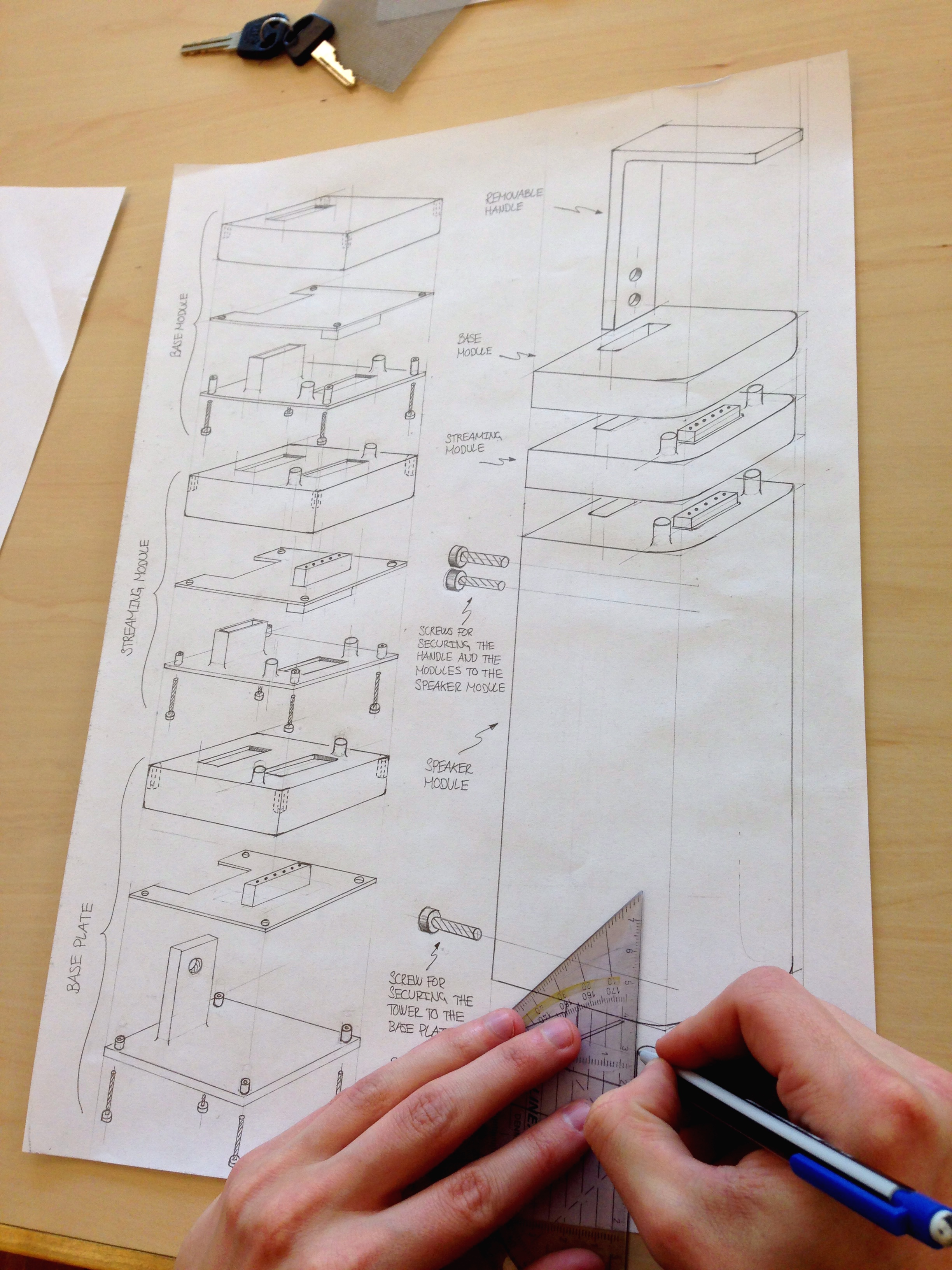
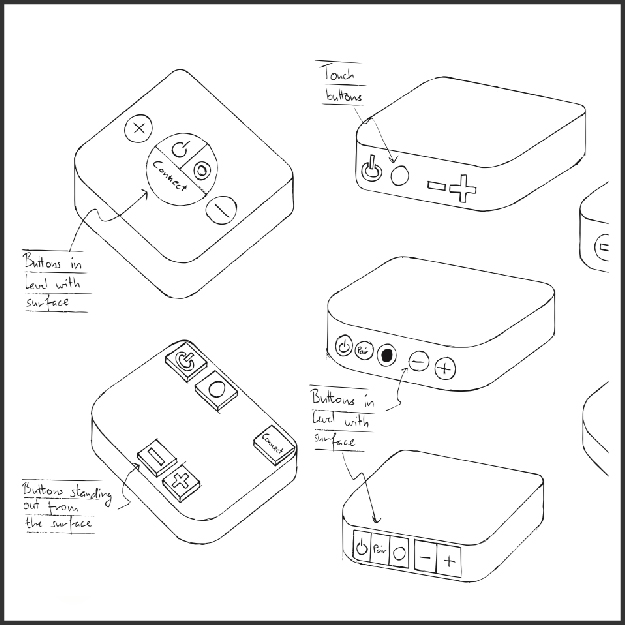
Time of Execution
2014
Client
Oticon A/S
Status
Completed and graded 12 (A+)
Design Team
Rasmus Brink Mårtensson, Frederik Hansen
Keywords
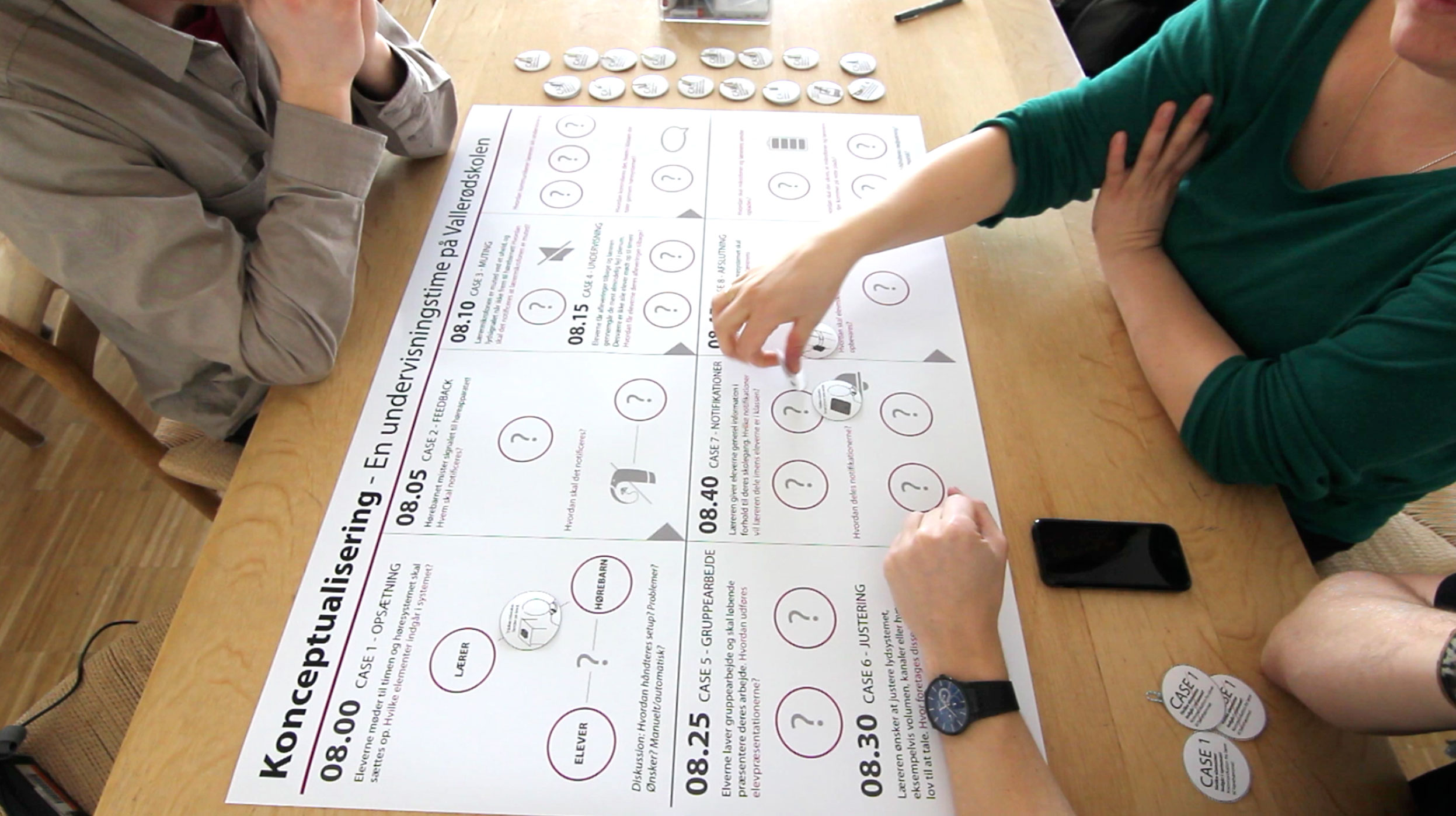
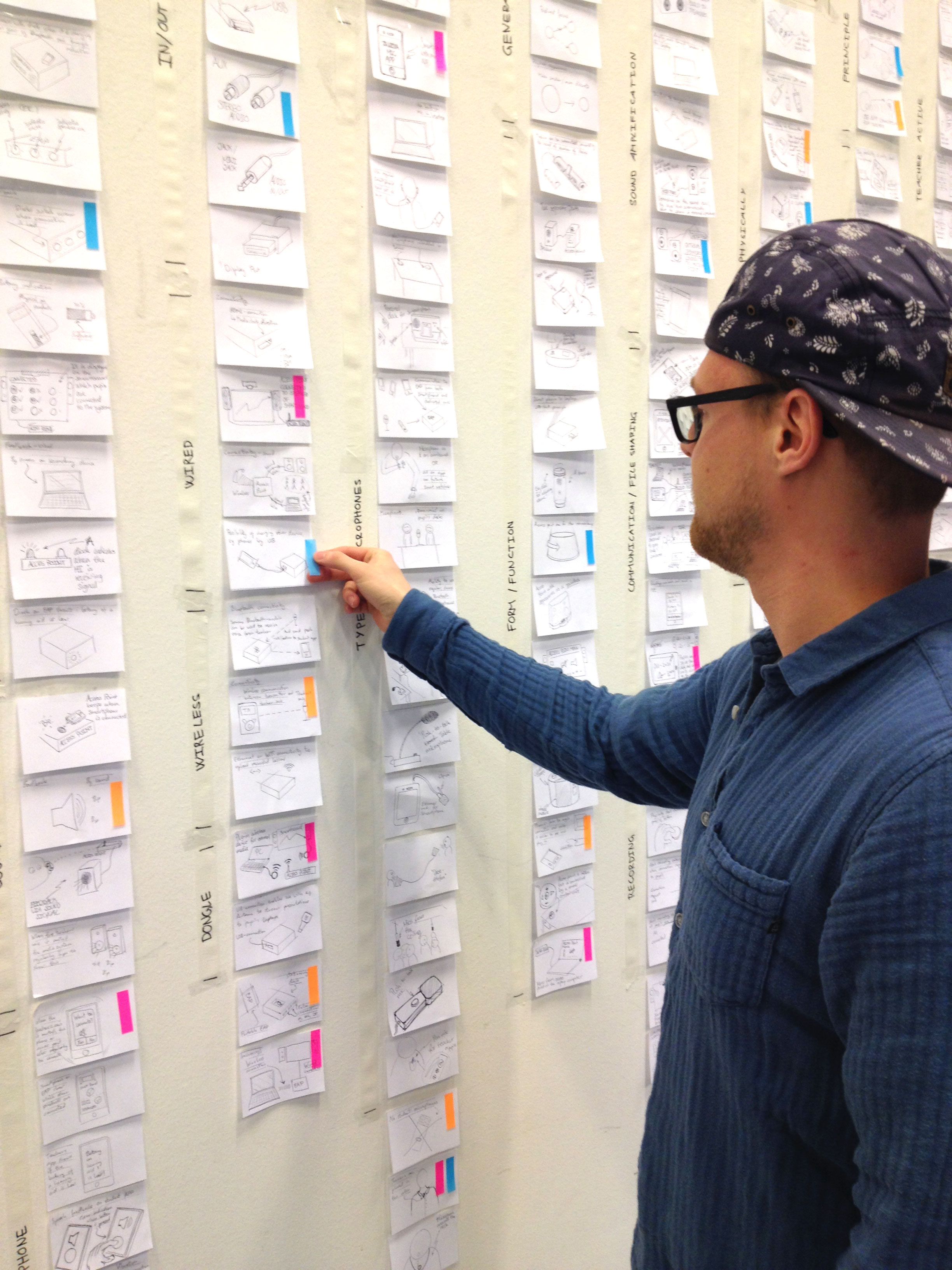
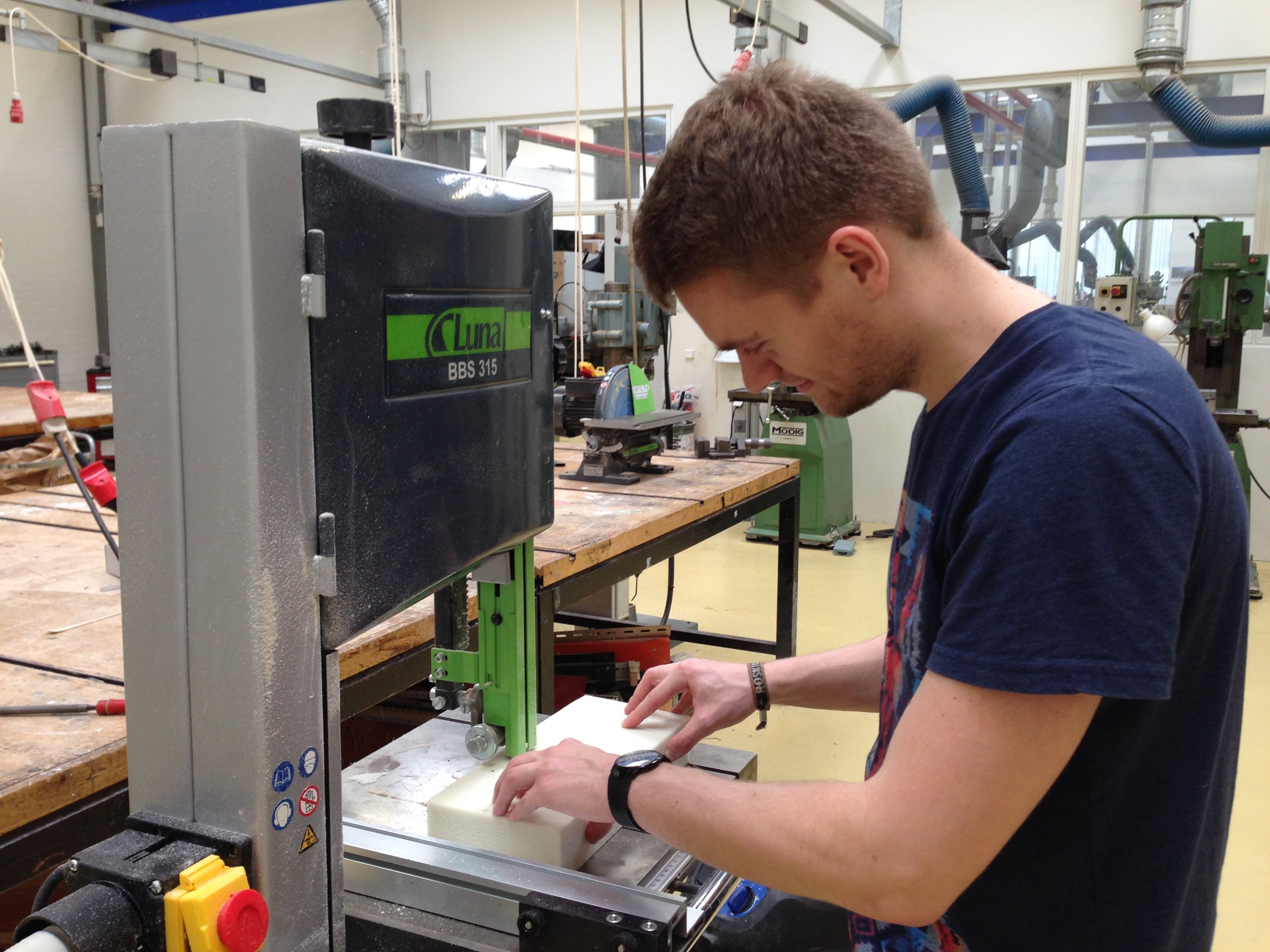
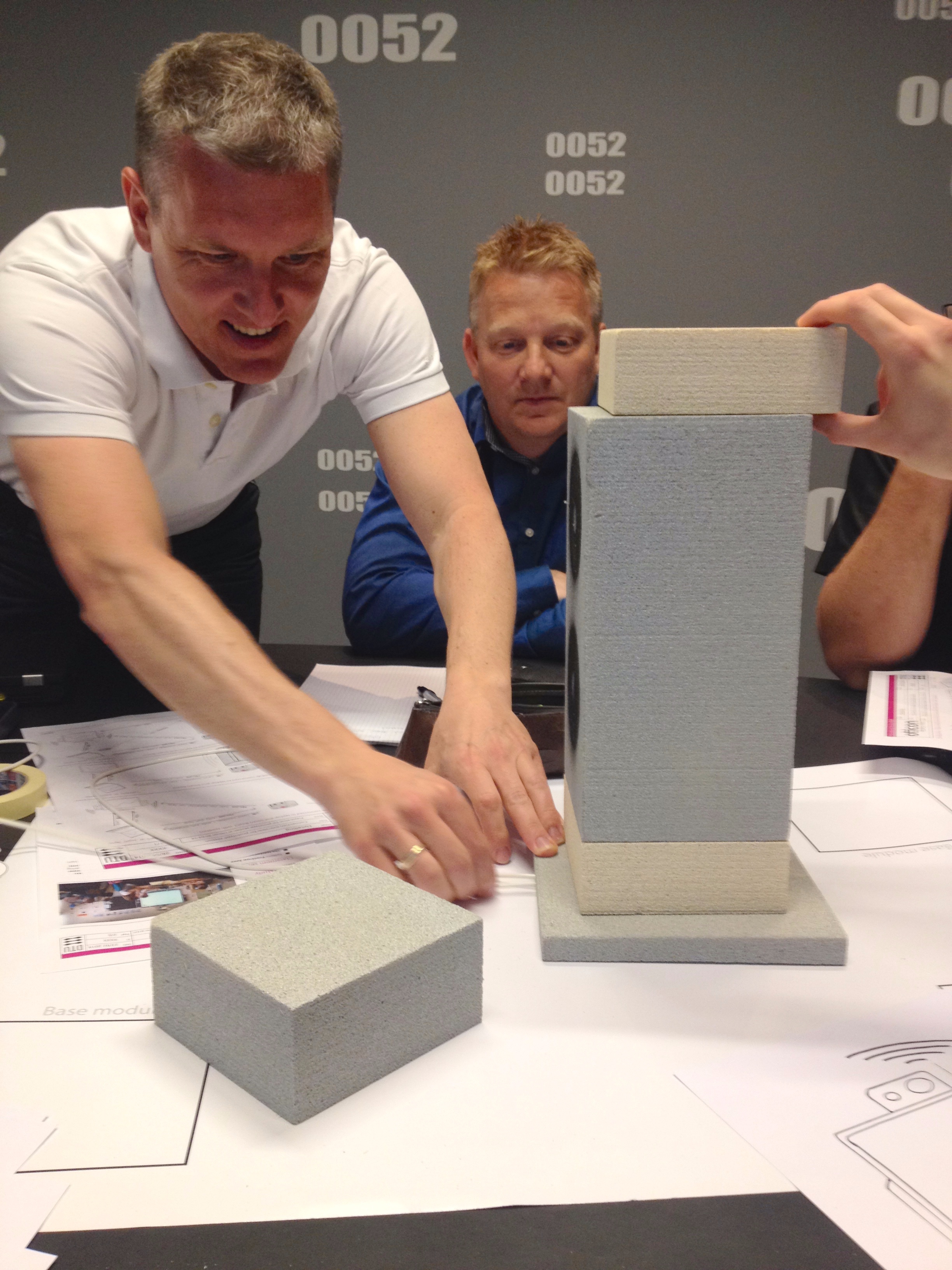
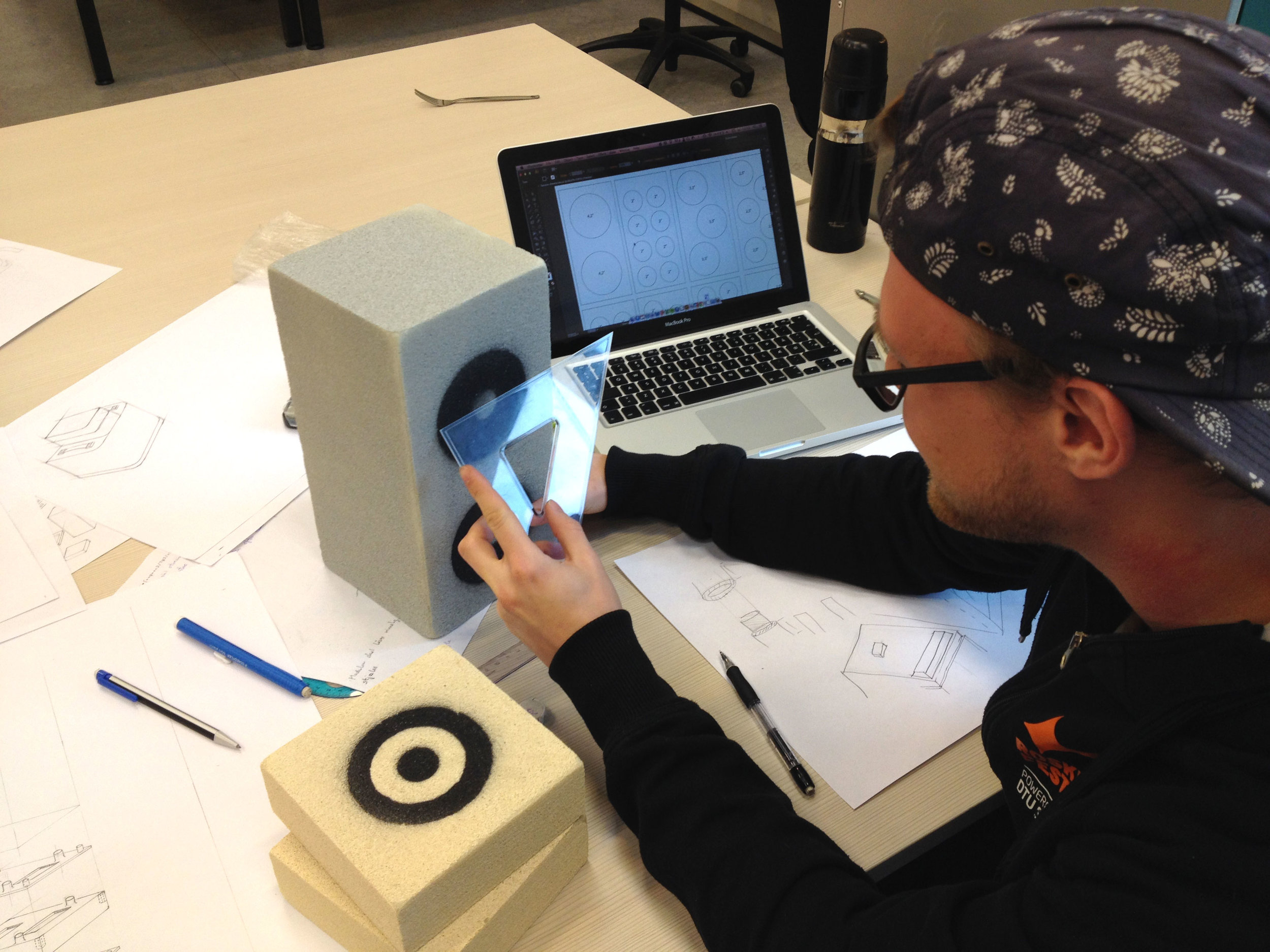
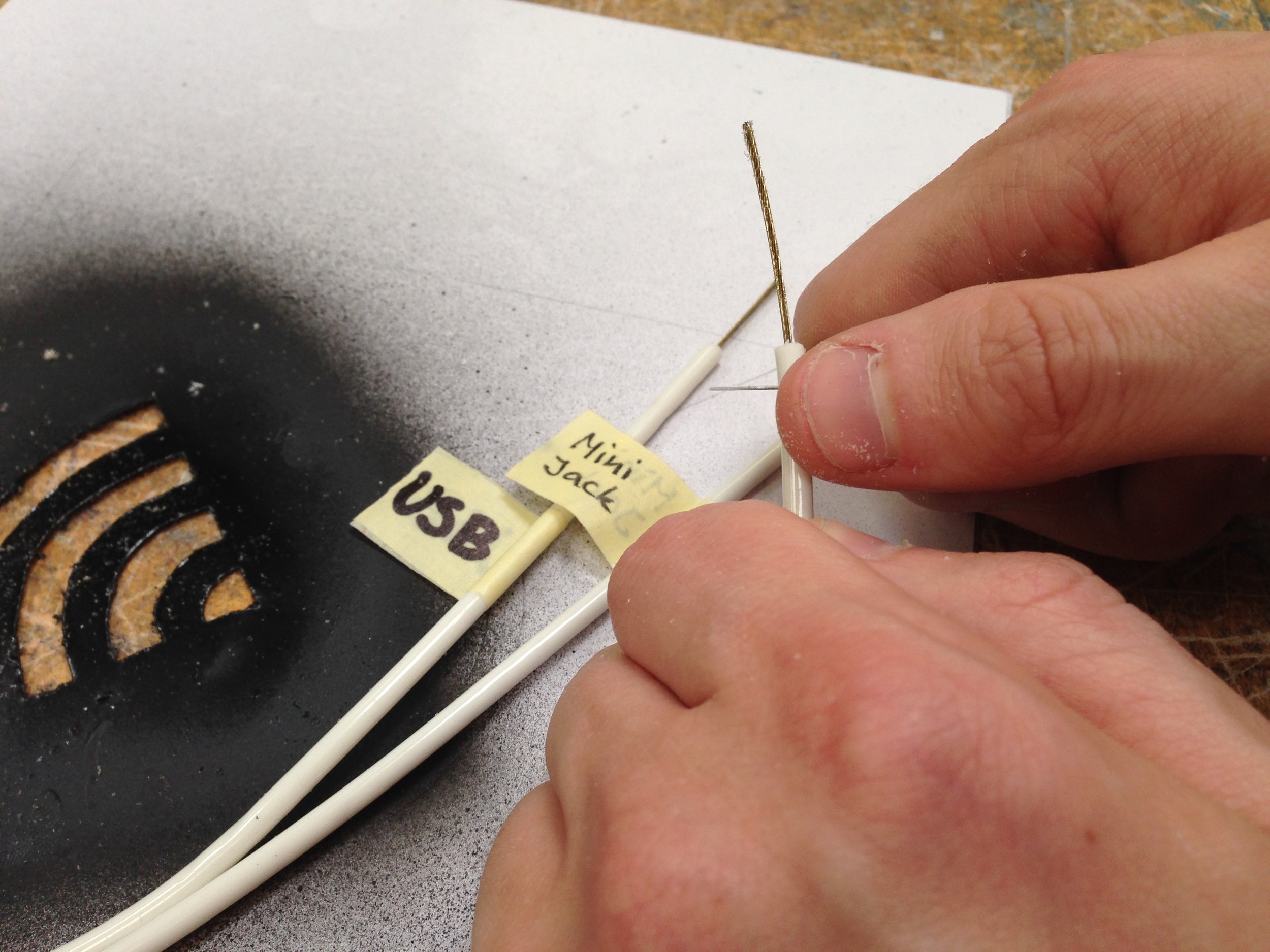
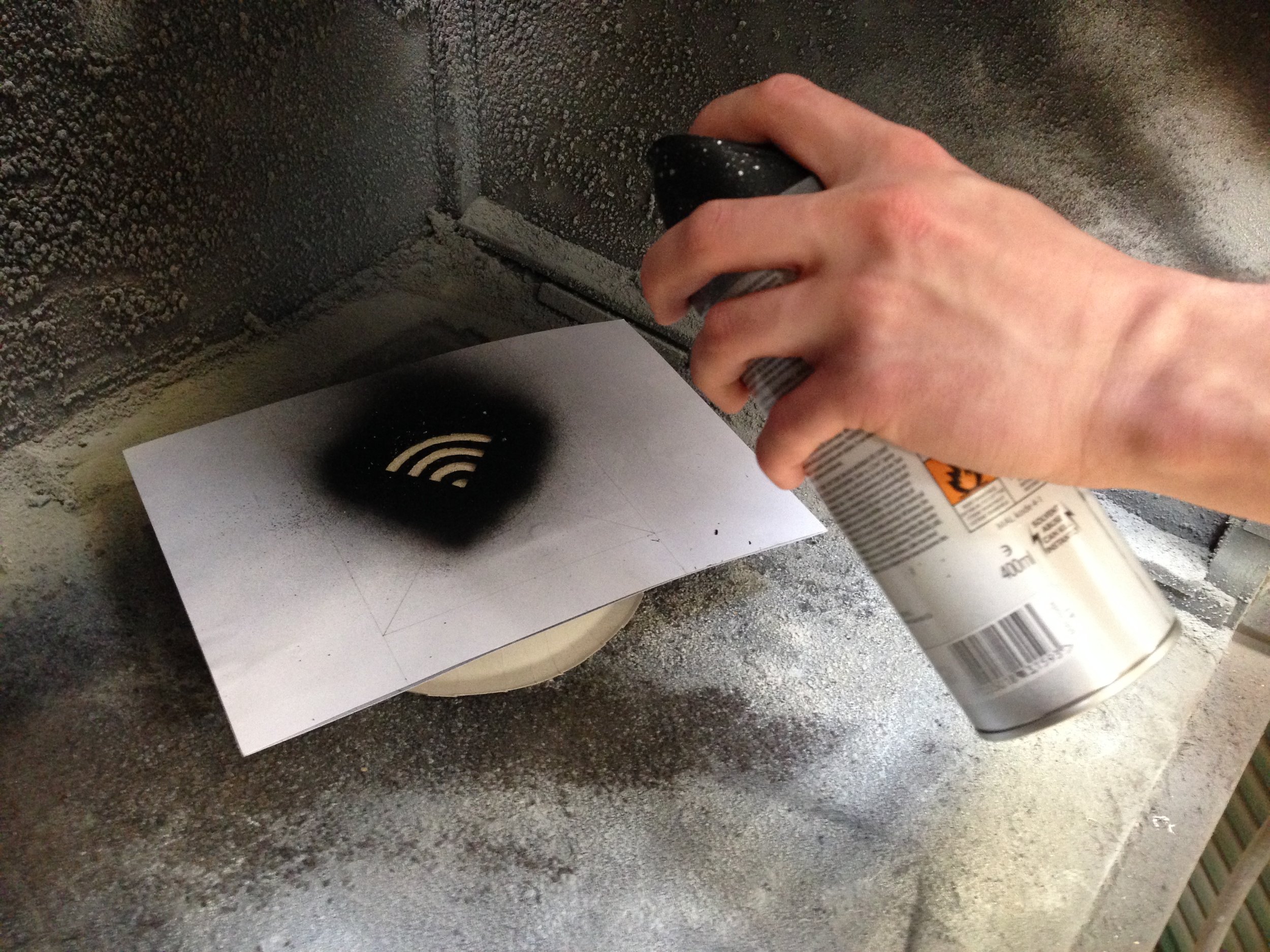
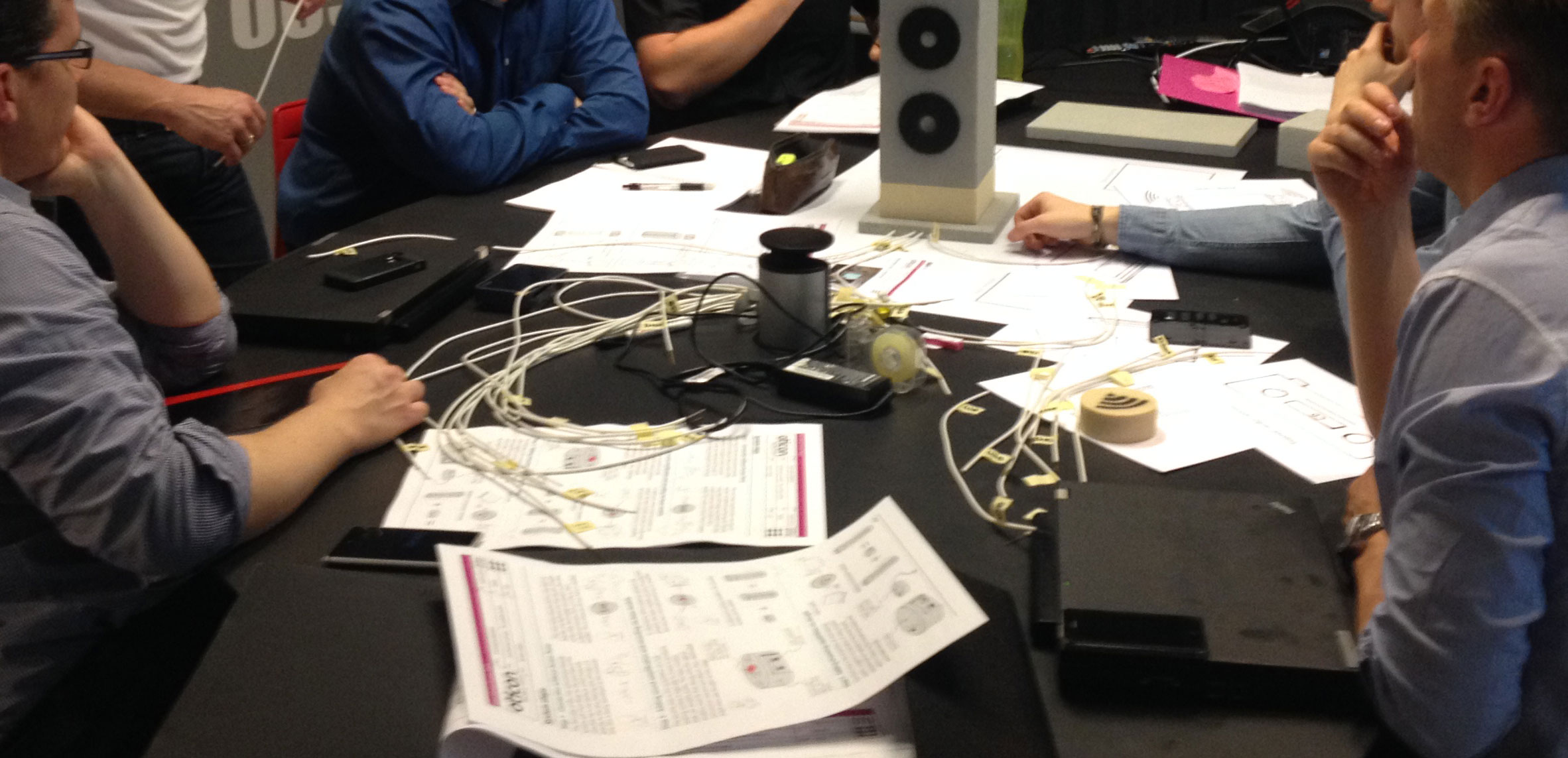
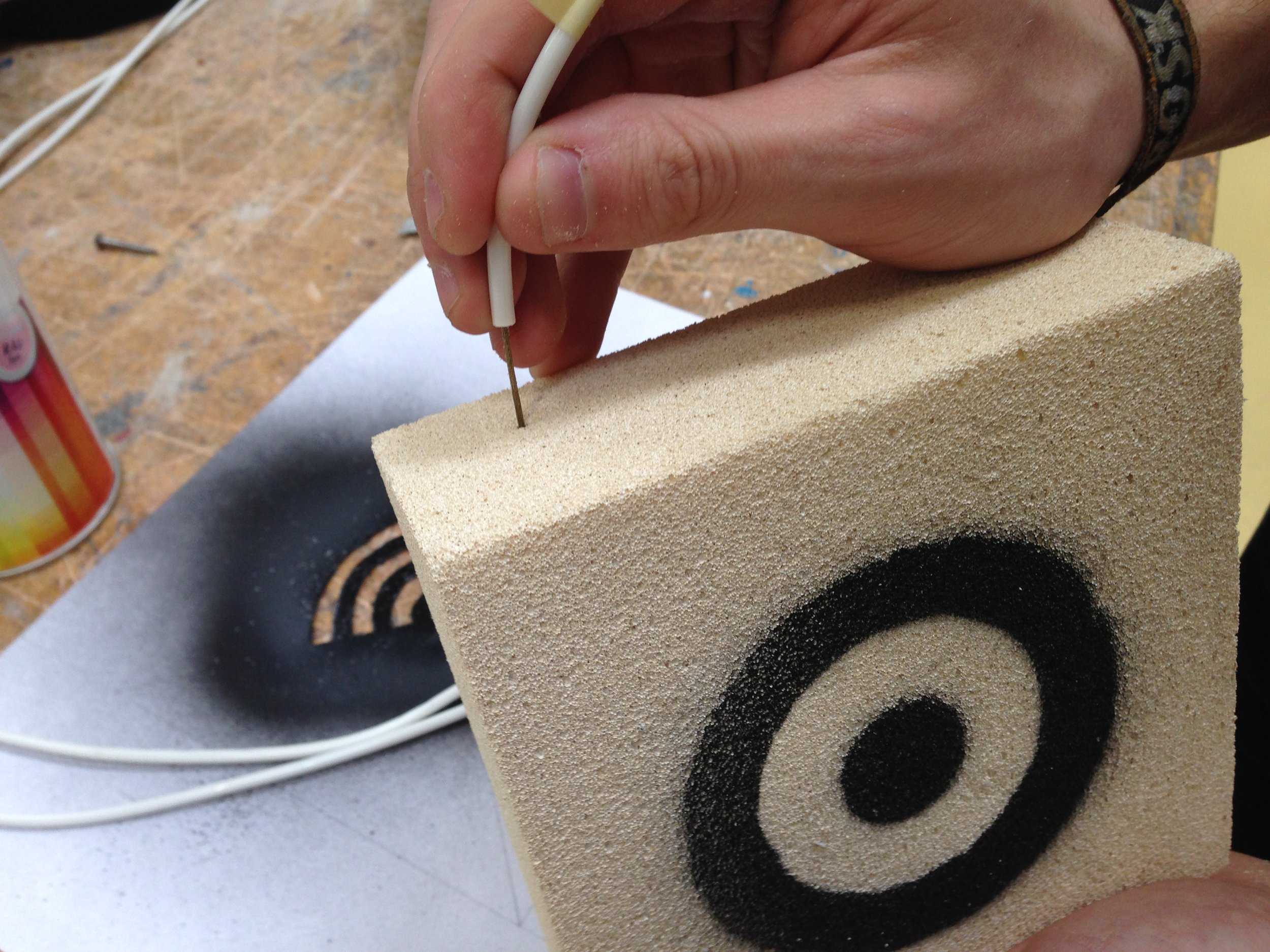
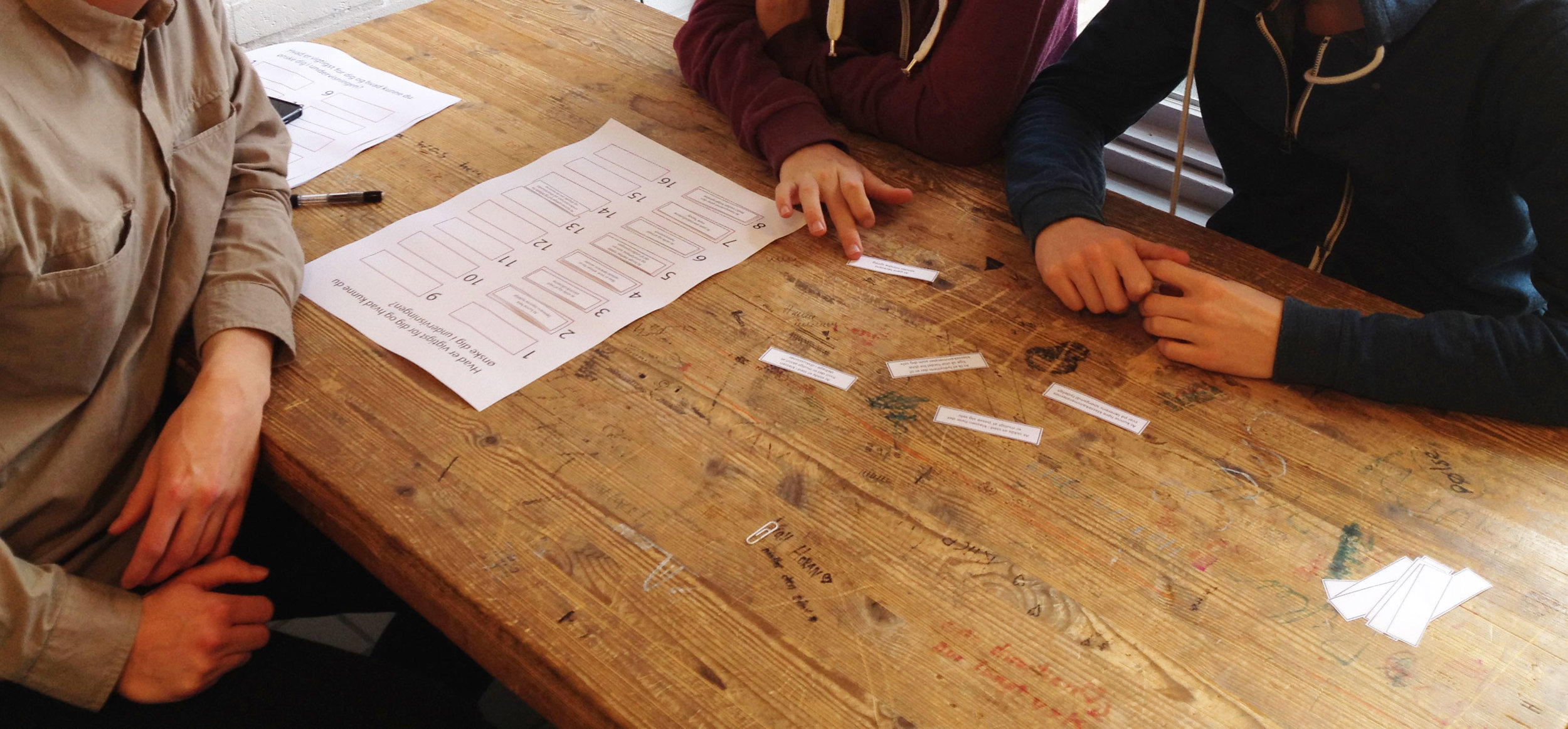
Interview Sessions, co-creative workshops, design games, systematic concept synthesis, hardware prototyping
Design Brief
“Our classmates think it is our fault”